
Human Intelligence @ Miami Herbert™
The Future of Work and Human Intelligence Skills
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and digital technologies is transforming the global workforce and the nature of work itself. As organizations and educational institutions navigate these changes, a growing consensus is emerging that the future of work will require a new mix of technical, digital, and human-centric skills. The World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Future of Jobs Report 2025 emphasizes that by 2030, nearly 39% of core skills needed for jobs are expected to change, with analytical thinking, technological literacy, resilience, and social influence among the most in-demand competencies. Similarly, research from McKinsey, KPMG, and leading academic studies underscores the urgent need for continuous upskilling, adaptability, and the integration of soft skills such as communication, teamwork, and ethical judgment into both business and educational programs (Babashahi et al., 2024; Cardon et al., 2023; KPMG, 2023).
Human Intelligence @Miami Herbert™
In line with the AACSB (2019) call to rebrand “soft” skills, Miami Herbert adopted a formal title to reflect the importance of these skills: "Human Intelligence @Miami Herbert™." A five-domain model was established using the University of Miami’s widely recognized CANES acronym: Communication, Analysis, Nurturance, Execution, and Strategy (see figure below). The central human skill emphasized across all domains is technological fluency, the ability to use digital tools and emerging technologies to complete tasks, solve problems, and quickly adapt as these tools disrupt workflows. When analyzing existing models and reviewing job postings, understanding technology, interpreting findings, and determining how best to apply it were common themes embedded across each domain. Each domain heading was determined through a systematic process that included coding and analyzing existing skill models and reviewing over 6,000 job postings to identify key thematic overlaps. Additional analysis is ongoing as corporate partner feedback is being gathered. The result is a set of five domains that promote the development of technological fluency and other human skills, continuously updated based on current job postings.
Click below for more information on the evolving Human Intelligence @Miami Herbert™ Framework.
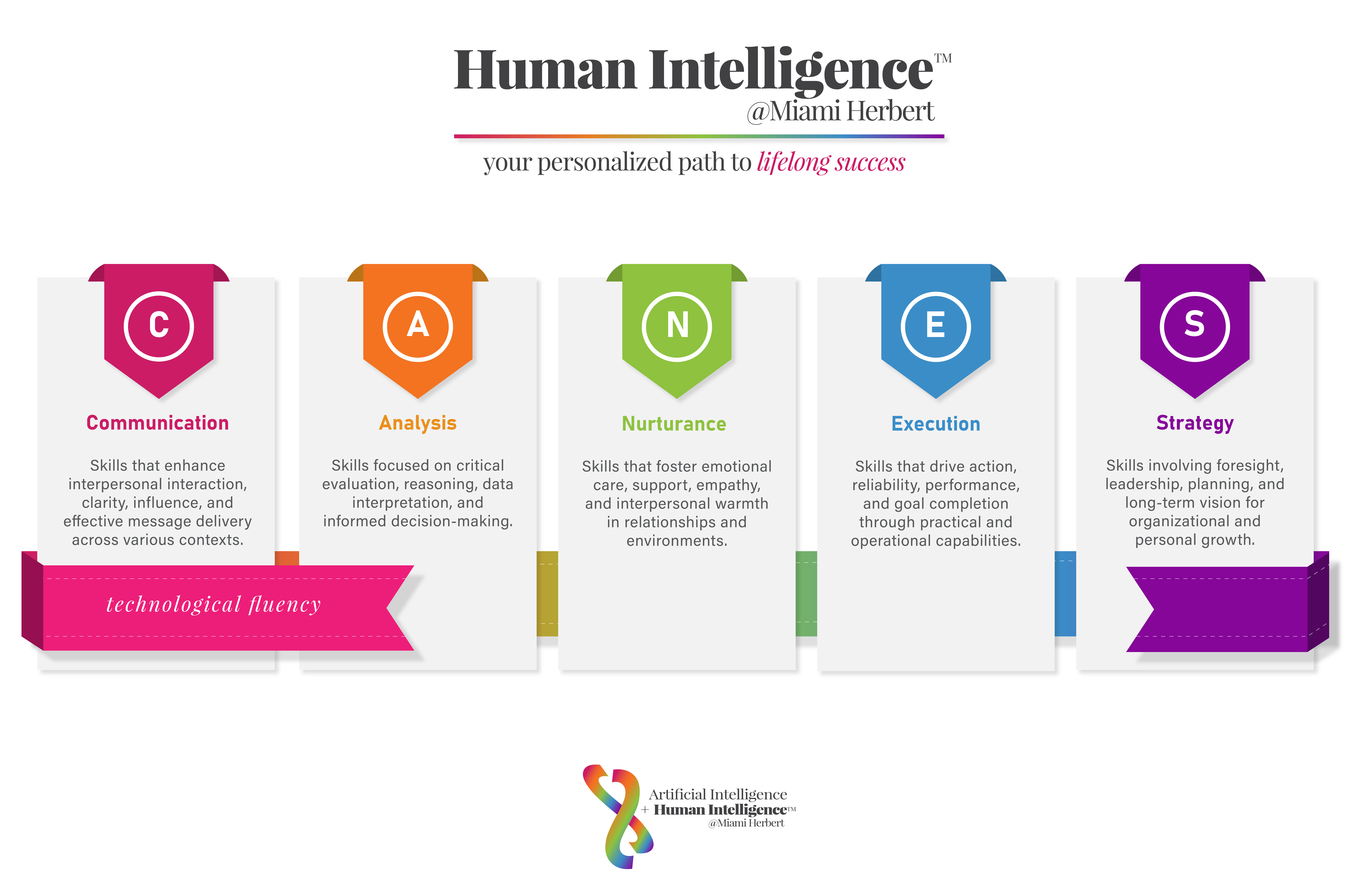
Skills that enhance interpersonal interaction, clarity, influence, and effective message delivery across various contexts. Alongside the core human skill of technological fluency emphasized across all domains, this domain tracks the following five key human intelligence skills.
- Trust & Influence
- Communication & Presentation
- Cultural Awareness
- Persuasion
- Relationship & Language Development
Skills focused on critical evaluation, reasoning, data interpretation, and informed decision-making. Alongside the core human skill of technological fluency emphasized across all domains, this domain tracks the following five key human intelligence skills.
- Strategical & Conceptual Thinking
- Critical Thinking & Reflection
- Data-Driven Decision Making
- Intuition & Ingenuity
- Problem Solving & Rational Thinking
Skills that foster emotional care, support, empathy, and interperonsal warmth in relationships and environments. Alongside the core human skill of technological fluency emphasized across all domains, this domain tracks the following five key human intelligence skills.
- Compassion
- Empathy
- Sense of Humor
- Socialization
- Emotional Intelligence
Skills that drive action, reliability, performance, and goal completion through practical and operational capabilities. Alongside the core human skill of technological fluency emphasized across all domains, this domain tracks the following five key human intelligence skills.
- Creativity & Adaptability
- Coordination Skills
- Executive Presence
- Teamwork
- Time Management
Skills involving foresight, leadership, planning, and long-term vision for organizational and personal growth. Alongside the core human skill of technological fluency emphasized across all domains, this domain tracks the following five key human intelligence skills.
- Growth Mindset
- Adaptive Leadership
- Consultative
- Design Thinking
- Goal Driven
Preparing Business Students for the Future of Work
Micro-credentials
Gen Z faces workforce challenges as employers expect technical and soft skills, but entry-level jobs often lack training and mentorship (Forbes, 2025). Microlearning has been shown to improve workplace training for Gen Z (Choudhary & Pandita, 2023). In higher education, micro-credentials provide focused certifications that develop industry-specific skills and can be updated quickly. For business students, these credentials complement core studies and enhance employability. Miami Herbert will introduce micro-credentials based on academic and labor market input, helping students deepen expertise in targeted skills and strengthening the program’s reputation.
This page will continue to be updated as the framework evolves and the dashboard is launched. Please check back regularly for the latest enhancements and information.
References
AACSB. (2019). Enough with Soft and Hard Skills: Let’s Get Smart and Sharp Instead.
Choudhary, H., & Pandita, D. (2023). Maximizing learning outcomes in the digital age: the role of microlearning for Gen Z. Development and Learning in Organizations: An International Journal.
Forbes. (2025). The Gen Z Catch-22: Workforce Challenges Threatening Careers in 2025.
McKinsey & Company. (2025). 2025 Learning Perspective: Development in the Future of Work.
World Economic Forum. (2025). Future of Jobs Report 2025.

